Table of contents
In this post, we will learn how to add Swagger documentation for APIs returning collections in NestJS. We will use @ApiProperty decorator to specify the type of the collection and its items.
UPDATE: NestJS v11
After NestJS v11 upgrade - using $ref property will cause a TypeScript error:
@ApiProperty({
type: 'object',
properties: { ['PERSON_ID']: { $ref: getSchemaPath(Person) } }, // $ref is causing type error
})
We have 2 options to solve this:
- Use
additionalPropertiesinstead ofpropertiesfield:
@ApiProperty({
type: 'object',
additionalProperties: {
allOf: [{ $ref: getSchemaPath(Person) }],
},
})
This fixes the type error. The downside here is that instead of having an explanatory key of 'PERSON_ID' in the Swagger example - we will have additionalProperty1, additionalProperty2 and additionalProperty3 keys with Person object in each key, which looks pretty overloaded, but type-safe.
- Continue using original approach with
@ts-expect-errorcomment:
$ref field is still part of ReferenceObject type from Open API spec. It is just omitted on the the @nestjs/swagger package level.
So original approach is still working. For those who accept @ts-expect-error comments in their projects - we can stick to original variant:
@ApiProperty({
type: 'object',
// @ts-expect-error $ref is existing field in SchemaObject
properties: { ['PERSON_ID']: { $ref: getSchemaPath(Person) } },
})
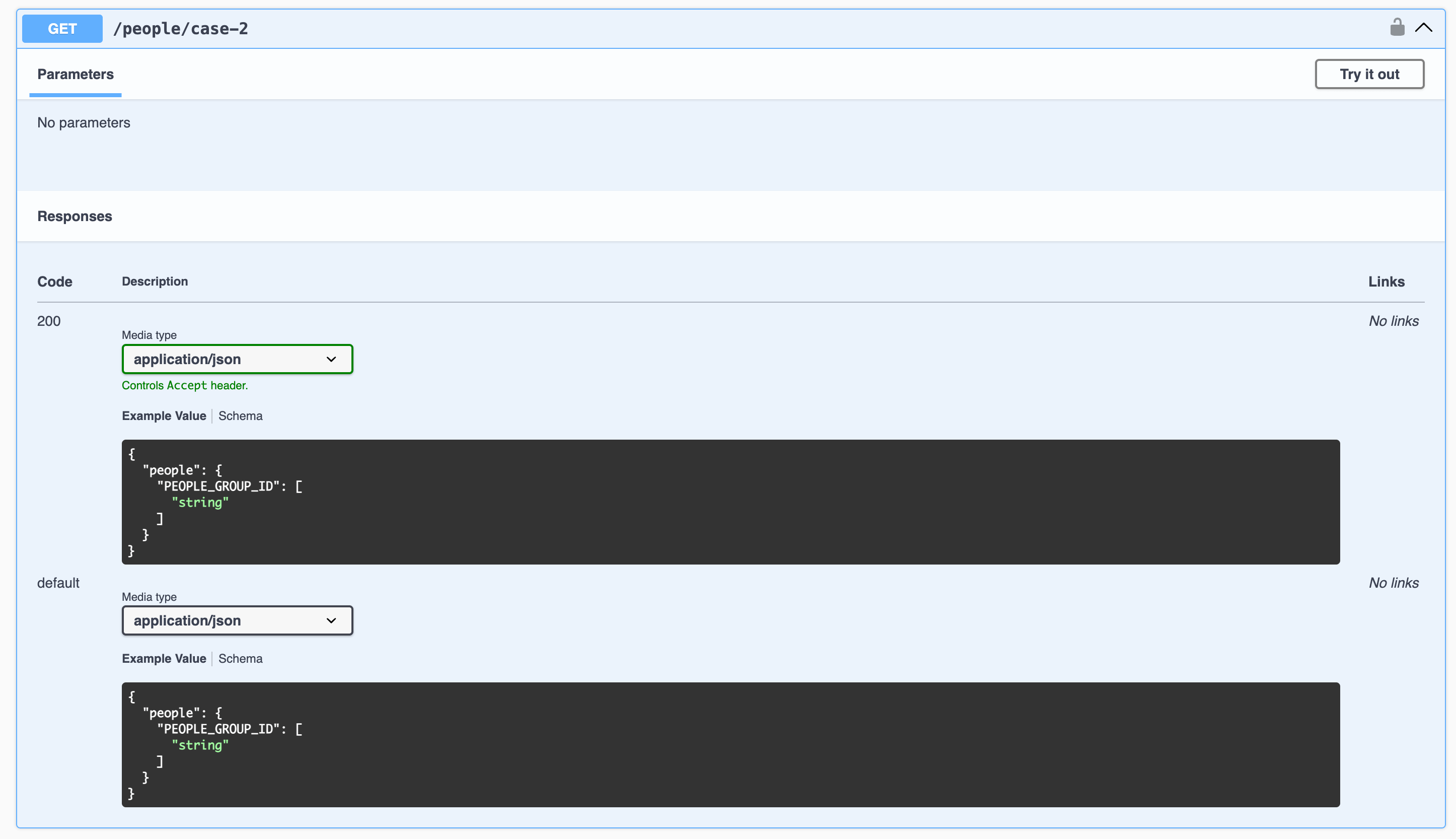
Case 1: API returns a collection of objects
Let's say we have an API that returns a collection of objects, normalized by some ID. We can use @ApiProperty decorator to specify the type of the collection and its items.
The API response will look like this:
{
"people": {
"1": { "name": "John" },
"2": { "name": "Doe" }
}
}
First, let's create a simple API that returns a collection of objects. (Here and below imports are omitted for brevity)
export class PeopleController {
@Get('case-1')
@ApiResponse({
type: People,
})
collectionOfObjects(): People {
return {
people: {
1: { name: 'John' },
2: { name: 'Doe' },
},
};
}
}
We are describing the return type by next DTO class:
@Controller('people')
export class Person {
@ApiProperty()
name: string;
}
@ApiExtraModels(Person)
export class People {
@ApiProperty({
type: 'object',
properties: { ['PERSON_ID']: { $ref: getSchemaPath(Person) } },
})
people: Record<string, Person>;
}
We described the People class with @ApiProperty decorator. We specified the type of the collection and its items. We also used @ApiExtraModels decorator to specify the extra models that are not directly referenced in the API.
The Swagger documentation for the API will look like this:
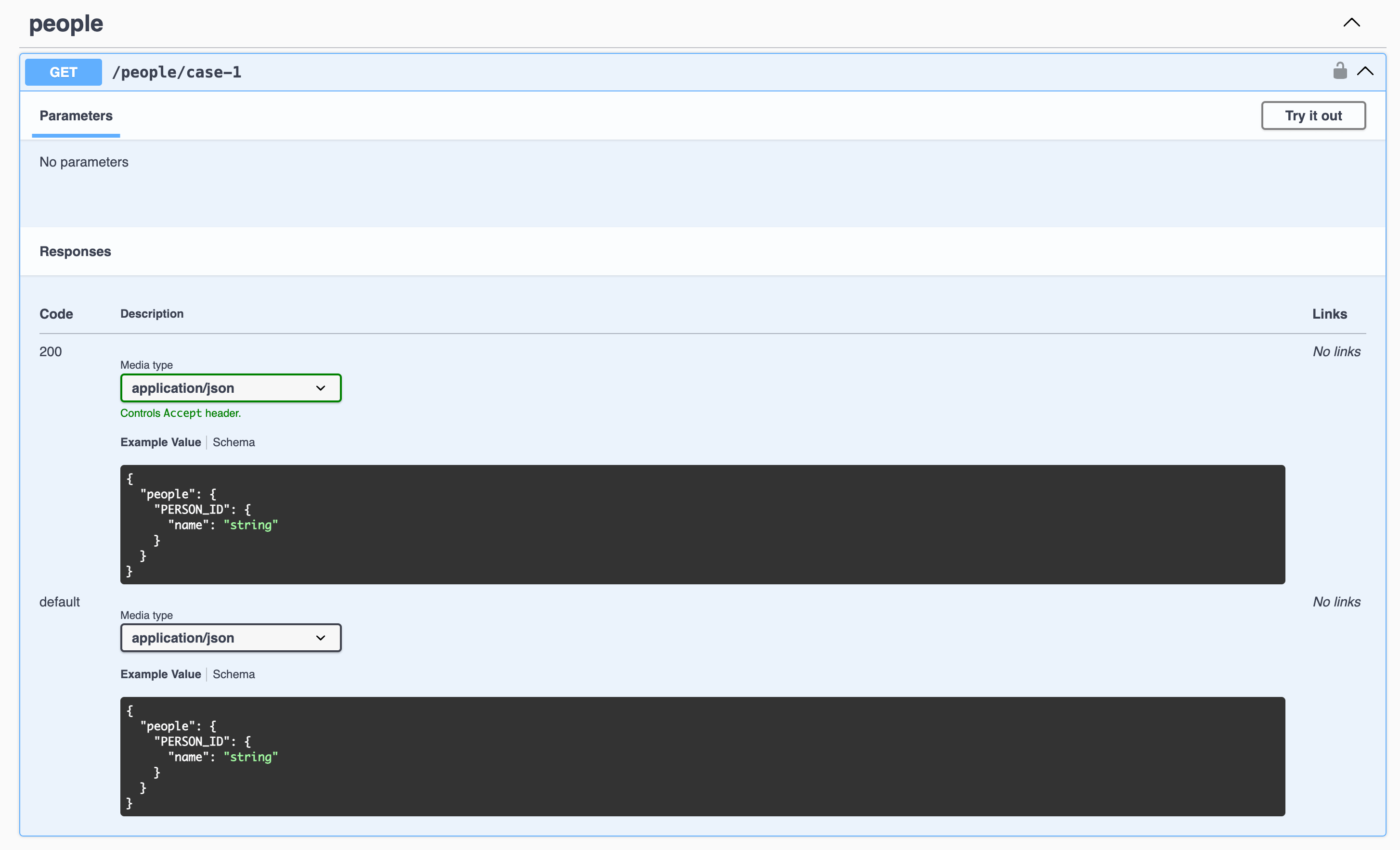
Case 2: API returns a collection of arrays of strings
Let's say we have an API that returns a collection of arrays of strings.
The API response will look like this:
{
"people": {
"1": ["John", "Doe"],
"2": ["Jane", "Doe"]
}
}
First, let's create a simple API that returns a collection of arrays of strings.
@Controller('people')
export class CatsController {
@Get('case-2')
@ApiResponse({
type: PeopleArray,
})
collectionOfArrays(): PeopleArray {
return {
people: {
1: ['John', 'Doe'],
2: ['Jane', 'Doe'],
},
};
}
}
We are describing the return type by next DTO class:
export class PeopleArray {
@ApiProperty({
type: 'object',
properties: {
['PEOPLE_GROUP_ID']: {
type: 'array',
items: { type: 'string' },
},
},
})
people: Record<string, string[]>;
}
The Swagger documentation for the API will look like this: